user manual

The weather in Micro Flight is designed especailly to simulate the weather conditions from a light aviation perspective.
There are two weather screens in Micro Flight, basic and advanced, the basic is used to control all weather conditions, and the advanced is used for more subtle parameters.
Press change weather menu to show the following screen:
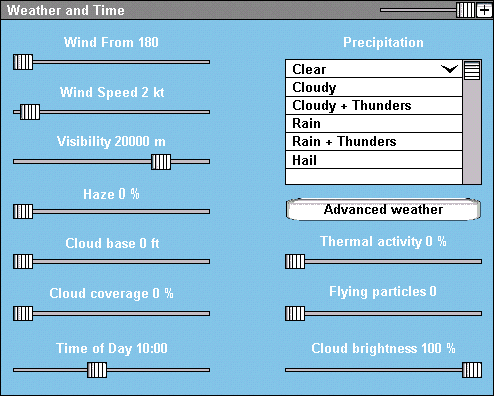
The basic weather screen adjusts:
- Wind direction - the direction from which the prevailing wind is blowing.
- Wind speed - speed of the prevailing wind.
- Visibility - maximum visibility of the ground when flying below the cloud base.
- Haze - degree of atmospheric clarity, the more hazy the less contrast will be seen.
- Cloud base - base of the clouds and the top part of thermal effects and haze effects.
- Cloud coverage - amount of sky covered by clouds.
- Time of day - time at the scene.
- Precipitation - type of precipitation in the scene, provided sufficient cloud coverage is set.
- Thermal activity - frequency of random thermals in the scene.
- Flying particles - number of flying particles that drift with the wind.
- Cloud brightness - controlls the brightness of clouds, can be used to make the scene look more realistic with different precipitation conditions.
Press the advanced weather button to show the following screen:
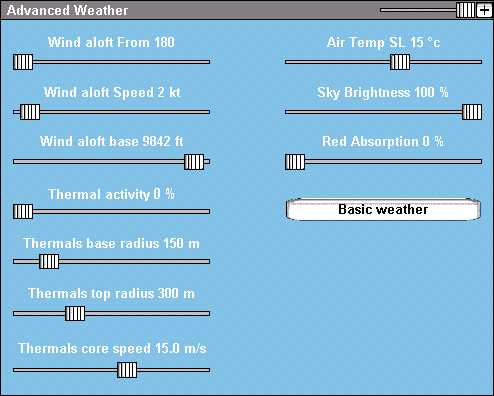
The advanced weather screen adjusts:
- Wind aloft from - the direction from which the high wind layer is blowing.
- Wind aloft speed - speed of the high wind layer.
- Wind aloft base - base altitude for high wind layer, the transition between prevailing wind and high wind layer begins at this level.
- Thermal activity - frequency of random thermals in the scene.
- Thermals base radius - base radius of random thermals in the scene.
- Thermals top radius - top radius of random thermals in the scene.
- Thermals core speed - maximal core speed of random thermals in the scene.
- Air temperature - air temperature measured at sea level, this temperature is used to calculate actual air density and temperature at any given height.
- Sky brightness - the brightness of sky and lighting in the scene, used to make precipitation conditions look more real.
- Red absorbtion - the blueish appearance of fog in the scene, can be used to simulate humidity and other atmospheric effects.
A schematic view of the weather model can be seen in the following diagram:
